Parish Emergency Management Advisory Committee (PEMAC)
The Louisiana Homeland Security and Emergency Assistance and Disaster Act (Disaster Act) – Louisiana Revised Statute (LRS) Title 29:727 I. (1) – mandates that each Parish or Police Jury President, through the Parish Director of the Office of Homeland Security and Emergency Preparedness (OHSEP), form a Parish Emergency Management Advisory Committee (PEMAC). The purpose of the committee is to offer advice and counsel to the Parish or Police Jury President on homeland security and emergency management issues. It is also intended to ensure that planning between the State, Parish administration, Parish counsel, and all municipalities and agencies involved in emergency management is sustained in a consistent manner.
Functions + Goals
PEMAC members may advise the Parish or Police Jury President on such matters as planning, development, prioritization, coordination, and implementation of homeland security and emergency management measures such as:
- Hazard mitigation
- Emergency Preparedness
- Prevention
- Response
- Recovery
- Grant requests
- Expenditure of grant funds
Leadership
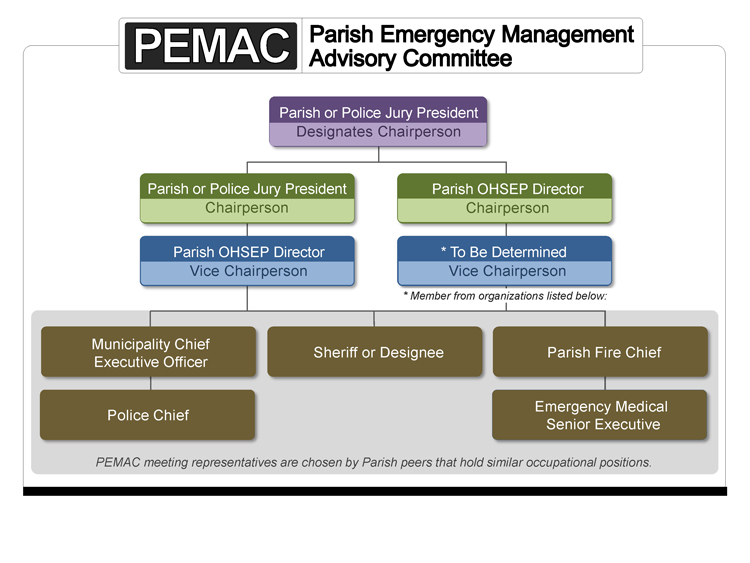
The Parish or Police Jury President either serves as chairperson or may designate the Parish Director of OHSEP to serve in his/her place. If the President serves as chairperson, the Director of OHSEP serves as the vice chairperson. Other members must include, at minimum, a Parish fire chief, a municipality chief executive officer, a police chief from within the Parish, the sheriff or his designee, and a senior executive from the emergency medical community. Peers in similar positions or occupations from across the Parish appoint PEMAC members to represent them in these meetings.
Meeting + Reporting Requirements
The committee must meet at least twice a year and submit a report to the Director of GOHSEP detailing potential issues within the Parish that relate to homeland security and emergency management.
Important Terms
Emergency Preparedness – Used in the context of this Manual, emergency preparedness means the mitigation of, preparation for, response to, and recovery from emergencies or disasters. It is called out in the Disaster Act as synonymous with “civil defense,” “emergency management,” and other related programs of similar names.
Hazard Mitigation – Hazard mitigation is any sustained action taken to reduce or eliminate future risk to people and property from natural and man-made disasters.
Recovery – Recovery also occurs in phases. Early phases of recovery include the rebuilding of infrastructure systems; the provision of adequate interim and long-term housing for disaster survivors; the restoration of health, social, and community services; promotion of economic development; and the restoration of natural and cultural resources. As defined in the National Disaster Recovery Framework (NDRF), long-term recovery is the complete redevelopment and revitalization of a disaster-impacted area. It includes the rebuilding or relocating of damaged or destroyed social, economic, natural, and built environments and a move to self-sufficiency, sustainability, and resilience by the community. Long-term recovery may continue for months or years.
Response – Typically, emergencies and disasters are discussed in phases. The response phase of an emergency involves immediate search and rescue, the safeguarding of property from further destruction or damage, and meeting immediate and basic human needs such as water, food, shelter, and medical attention.